Student HPC Guide
To connect to LU HPC, first establish a connection to the University of Latvia VPN.
- Gateway: vpn.lu.lv
- Username: LUIS Username
- Password: LUIS Password
Once the VPN connection to the University of Latvia is established, you can proceed to connect to the HPC server:
Note that to connect to the server, you must contact the LU HPC administrators to create a personal LU HPC account and working directory:
Username and password for LU HPC are not your LUIS credentials, but an account created by the administrators on the HPC server.
- ssh username@hpc.lu.lv
- Enter password
Slurm commands that may be useful on the HPC server:
- sinfo
- View available nodes, partitions, node status (e.g., idle, alloc, down, drain)
- squeue
- Shows all active SLURM jobs on the HPC server, including:
- JobID
- Partition
- Name
- User
- Time
- Node
- List
- squeue -u username
- View jobs for a specific user
- scancel JOBID
- Cancel a submitted SLURM job
- scancel -u username
- Cancel all active jobs of a user
Starting jobs and entering nodes:
For example, the command:
srun --partition=gpu-jp --nodelist=node-gpu --mem=32G --cpus-per-task=16 --pty bash
- Creates a job and opens a shell on the LU HPC GPU node
--mem=32G: allocates 32 GB RAM--cpus-per-task=16: allocates 16 CPU cores--pty bash: opens an interactive shell- Note that this type of job is mainly for testing; exiting the server will automatically terminate the job.
- To test GPU access, run
nvidia-smito view available graphics cards.
- To test GPU access, run
Long-running jobs
First, prepare an environment with required libraries—either build your own Docker images or use available containers.
For example, to pull a Singularity container with PyTorch and CUDA 11.8:
singularity pull docker://pytorch/pytorch:2.1.0-cuda11.8-cudnn8-runtime
After pulling, you will see a file in your home directory:
pytorch_2.1.0-cuda11.8-cudnn8-runtime.sif
To enter this Singularity container, run:
module load singularitysingularity exec --nv pytorch_2.1.0-cuda11.8-cudnn8-runtime.sif bash--nvenables NVIDIA GPU support so the container can see node GPUs.
To run a long job, use SBATCH by creating a shell script:
Below is an example SBATCH job script “run_pointnet.sh”
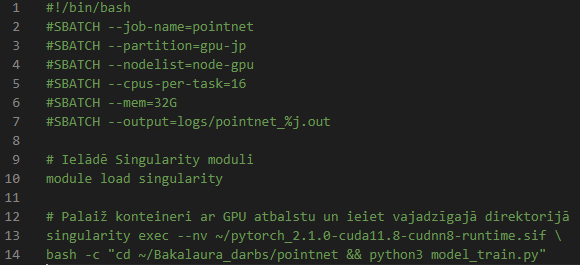
SBATCH arguments are similar to the earlier srun command:
srun --partition=gpu-jp --nodelist=node-gpu --mem=32G --cpus-per-task=16 --pty bash
After submitting the script, you can monitor the job with:
squeue– check if the job has startedtail -f logs/pointnet_$jobid.out- Follow the log output (e.g., output from print() in your script).
- If the job crashes, error messages will appear here.
- To cancel the job, use
scancel $jobid- Find the job ID via
squeue
- Find the job ID via
Prepared by Jānis Sausais, 4th-year student.